Becoming a dentist in Canada is a good yet challenging process that requires dedication, thorough education, and need to follow standard regulatory rules and regulations . This comprehensive guide explain the steps in becoming a dentist, highlights the fastest way to become a dentist, and details the process for international dentists seeking certification. It also covers Canada dentistry schools, dental education in Canada, and basic insights into how much a dentist make in a year .

Step-by-step guide to becoming a licensed dentist in Canada (For Canadian resients )
Step 1 : Complete high school with strong academic performance
The foundation for a career as a dentist in Canada begins in high school . The students who want to become a dentist in Canada , should focus on , science and mathematics subjects including biology, chemistry, physics, and calculus . These subjects build up the base for what you need to become a dentist . A high school diploma or equivalent , such as a General Educational Diploma (GED) , is essential for advancing to post-secondary education . Know the difference between GED and high school diploma here .
- Tips : Maintain a high GPA to strengthen your university applications. Engage in extracurricular activities, such as volunteering or science clubs, to show multitalented skills.
Get the latest updates on NDEB licence exams
Step 2: Get a bachelor’s degree
Most dental schools in Canada require applicants to complete minimum three years of undergraduate education , though a four-year bachelor’s degree is often preferred. While no specific major is compulsory, but degrees related to medical sciences like in Biology, chemistry, and related subjects, align closely with dental school requirements ..
- Prerequisites: Common requirements include courses in biology, general and organic chemistry, physics, and sometimes English or humanities. Check the specific requirements of your target Canadian dentistry schools, as they may have different requirement .
- Duration: Typically, 3–4 years long degree required .
- Tips: Generally high GPA is required (ideally 3.5 or above) to remain competitive. Join clinic or any volunteer organisation to get familiar with dentistry and there you can do minor dental procedure .
Step 3: Write the Dental Aptitude Test (DAT)
The Dental Aptitude Test (DAT), arranged by the Canadian Dental Association (CDA), is a vital component of dental education in Canada. This test identify critical thinking , knowledge level , physical functioning of the body and mind, which are essential for dental practice, as a dentist deals with different types of patients from different backgrounds and also in dentistry most of the task has to be performed by dentist themselves.
- When to Take It: Prior planning is must , Most students take the DAT in their third or final year of undergraduate studies, typically in February or November.Follow CAD .
- Preparation: Invest in DAT prep courses or materials to achieve a competitive score (e.g., 20 or higher on a scale of 1–30).
- Cost: Approximately $540 CAD (subject to change).
- Tips: Register early, as there are limited seats available. Strong DAT scores increase your chances of admission to dental schools in Canada.
Step 4: Join a accredited dental school
Canada has 10 accredited dental schools in Canada, recognized by the Commission on Dental Accreditation of Canada (CDAC). These include:
- University of Alberta (School of Dentistry)
- McGill University (Faculty of Dentistry)
- Université de Montréal (Faculté de médecine dentaire)
- Université Laval (Faculté de médecine dentaire)
- University of Saskatchewan (College of Dentistry)
- University of British Columbia (Faculty of Dentistry)
- University of Manitoba (Faculty of Dentistry)
- Dalhousie University (Faculty of Dentistry)
- University of Toronto (Faculty of Dentistry)
- Western University (Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry)
Dental education in Canada typically involves a 4 years Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) program. These programs combine regular full time classroom learning, onsite laboratory work, and onsite clinical practice.
- Admission Requirements: A strong GPA, competitive DAT scores, letters of recommendation from authoritiesties , a personal statement, and sometimes a personal interview. Some schools, like McGill, may require proficiency in French along with English .
- Tuition Costs: Vary widely, ranging from $15,000 to $60,000 CAD per year, depending on the institution and residency status. It changes from time to time . Contact to concerned school as I have provided the school’s links above.
- Tips: Apply to multiple schools to increase your chances to get addmission. Research about each school and join which align to your career goal.
Step 5: Complete the National Dental Examining Board (NDEB) certification
After graduating from an accredited dental program, you have to write the exams to get NDEB certification, which is must to get licence in any province and territory of Canada to practice as a dentist in province and territories . This is the National exam which access you dentist knowledge you have gained in school . It access both theoratical and practical knowledge at clinic like setup . The NDEB certification process includes:
- Written Examination: A 150-question multiple-choice exam testing theoretical knowledge in clinical sciences, dental materials, and ethics. A minimum scaled score of 75 is required to pass.
- Virtual Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE): A summative exam assessing problem-solving and decision-making skills through clinical scenarios. It can be taken up to four months before graduation, with results valid upon proof of graduation.
- Cost: Approximately $2,500–$3,000 CAD for both exams. To get approximate idea about cost , you can use our free Cost Estimator Tool
- Tips: Prepare thoroughly using NDEB study resources. A study resources guide is available at NDEB website. Passing both exams grants NDEB certification, which is recognized nationally and does not expire.
Step 6: Obtain provincial licensure
Dentistry is a regulated profession in Canada, and each province has its own Dental Regulatory Authority (DRA) responsible for licensure. After NDEB certification, you must apply for a license in the province where you want to practice.
- Common Requirements:
- Proof of NDEB certification.As we have discussed earlier .
- Completion of a Jurisprudence and Ethics course (e.g., in Ontario, through the Royal College of Dental Surgeons of Ontario (RCDSO).
- Evidence of language proficiency (English or French, depending on the province, such as Quebec requiring French).
- Good standing with no prior disciplinary actions.
- A list of DRAs can be found here.
- Tips: Contact the DRA early to understand additional requirements, such as fees or background checks. Some provinces may require a practical exam or interview. DRAs make changes regularly so keep in mind , to get current information , contact them directly .
Step 7: Consider Specialization (Optional)
After becoming a licensed dentist in Canada, you may go to specialize in one of nine recognized dental specialties programs , which are listed here. Specialization requires:
- Additional Education: 2–5 years of postgraduate training in a CDAC-accredited program.
- National Dental Specialty Examination (NDSE): Administered by the Royal College of Dentists of Canada (RCDC).
- Cost and Duration: Varies by specialty. Contact “The Royal college of Dentists of Canada” .
- Tips: Specialization can boost your skill and knowledge and also salary as a specialist dentist in Canada, but it’s not compulsory for general dental practice in Canada.
Fastest Way to Become a Dentist in Canada
The fastest way to become a dentist typically takes 7–8 years in Canada:
- 3-Year Undergraduate Degree: Some dental schools accept students after three years of undergraduate study, provided prerequisites are met.
- 4-Year Dental Program: Enroll in a DDS/DMD program directly after your bachelor’s degree.
- NDEB and Licensure: Complete NDEB exams during your final year and apply for licensure immediately after graduation.
To accelerate the process:
- Choose a science-related undergraduate major to streamline prerequisites.
- Prepare for the DAT early to avoid retakes.
- Apply to schools with rolling admissions to secure a spot sooner.
However, rushing may compromise GPA or DAT performance, so balance speed with quality preparation.
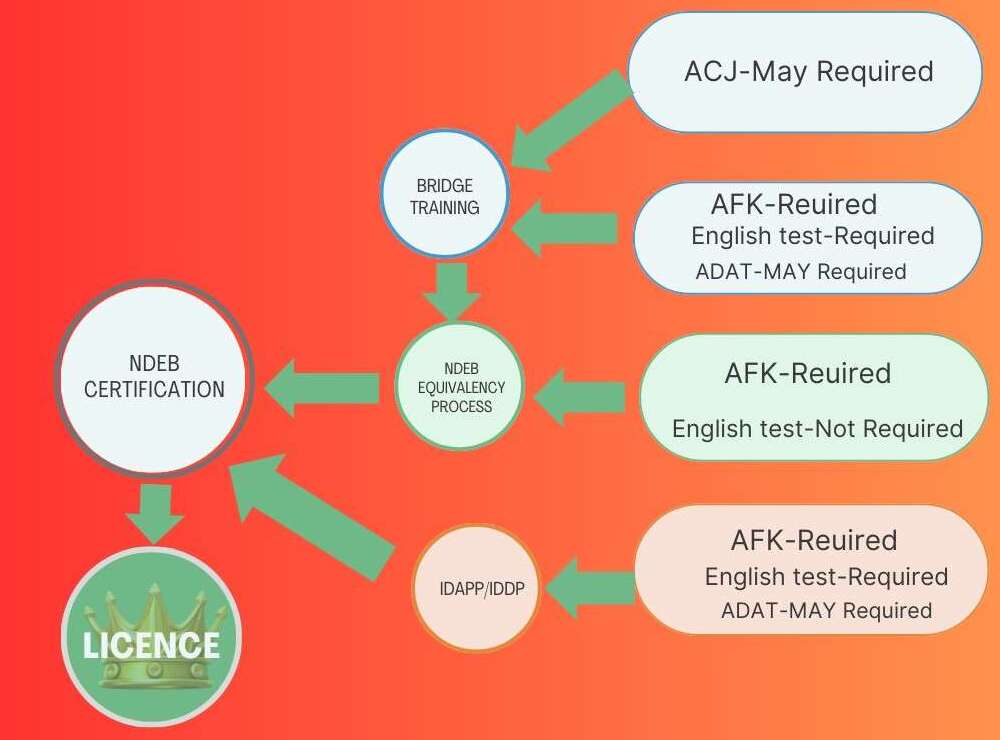
Certification process for international dentists
Internationally trained dentists (ITDs) face additionalchallanges to become certified dentists in Canada, as degrees from non-accredited programs (not recognized by CDAC) require equivalency or further education in Canada schools . There are two options for a ITDs :
Option 1: NDEB Equivalency Process
The NDEB Equivalency Process allows internationally trained dentists to demonstrate competency equivalent to Canadian graduates.
- Apply to NDEB:
- Submit proof of a dental degree from a recognized institution. Go to the NDEB , to know guidelines to submit the credentials .
- Pay an application fee (approximately $800 CAD, Go to NDEB website to know the current fee , as NDEB make frequent changes ).
- Await acceptance, which may take weeks due to verification.
- Assessment of Fundamental Knowledge (AFK):
- A written multiple choice type of exam testing basic dental knowledge.
- Exam fee : $1,000 CAD.
- Passing marks are 75 percentile based on the standard set by NDEB. After passing AFK , you can proceed to next step
- Assessment of Clinical Judgment (ACJ):
- Evaluates diagnostic and treatment planning skills through case-based scenarios. It access the practical knowledge and application in a real world.
- Cost: $1,300 – $1500 CAD.
- National Dental Examination of Clinical Competence (NDECC):
- A practical exam assessing clinical skills in a simulated environment.
- Cost: $7,000 CAD.
- After passing all these three exams , you can go to certification process (Written and Virtual OSCE). . Certification process is same for all who have completed their graduation in Canadian accredited schools or International dentist who have pass all three exams AFK,ACJ and NDECC.
- Complete NDEB Certification and Licensure:
- Follow the same steps as Canadian graduates for NDEB exams and provincial licensure.
- Duration: 2–3 years, depending on exam scheduling and preparation.
- Tips: Enroll in preparatory courses provided by us Online to improve exam performance. Budget for high costs, as the total process may exceed $15,000 CAD.
Use our free Cost Estimator Tools

Option 2: Enroll in a Bridging or Qualifying Program
Some dental schools in Canada provide bridging programs to fullfil the knowledge gap between graduates from ITDs and graduates from Canadian schools , such as the International Dentist Advanced Placement Program (IDAPP) at the University of Toronto or the Advanced Standing Program at Western University. These programs facilitate ITDs into the DDS/DMD programs .
- Eligibility: A dental degree from a recognized institution and, often, passing the AFK.
- Duration: Typically 2 years, placing students in the third year of a DDS/DMD program.
- Cost: $50,000–$100,000 CAD, depending on the program.
- Outcome: Graduates receive a DDS/DMD degree, qualify for NDEB exams, and can apply for licensure.
- Tips: Research program availability early, as spots are limited. Demonstrate strong clinical experience to enhance your application.
Option 3: Reapply to a Canadian Dental School
If equivalency or bridging programs are not viable, international dentists can apply to a four-year DDS/DMD program as a new student. This is less common due to the time and cost but ensures full accreditation.
- Pros: No additional equivalency exams required before NDEB certification.
- Cons: 4 years of study plus high tuition costs ($100,000–$200,000 CAD total).
How much a dentist make ?
The salary for a dentist in Canada varies based on experience, location, and specialization. According to recent data:
- Average Salary: $130,000–$160,000 CAD per year for general dentists.
- First-Year Associates: Start at approximately $120,000–$150,000 CAD.
- Specialists: Earn $200,000–$350,000+ CAD annually, with oral surgeons and orthodontists at the higher end.
- Regional Differences:
- Highest: In Manitoba and Saskatchewan dentist income is highest ($140,000–$160,000 CAD median).
- Lowest: British Columbia and Alberta , dentist has lowest salary ($100,000–$120,000 CAD median).
- Clinic Owners: Potential to earn more then $250,000+ CAD with established practices.
Dentist salaries in Canada are influenced by factors such as patient volume, private vs. public practice, and urban vs. rural settings. The demand for dental professionals ensures job stability and competitive compensation.
Challenges and considerations
- Financial Commitment: Dental education in Canada is expensive, with total costs (undergraduate + dental school) often exceeding $200,000 CAD. Explore scholarships, bursaries, or student loans, such as the Canada Student Loan Program.
- Time Investment: The process spans 7–10 years for Canadian students and potentially longer for international dentists.
- Competitive Admissions: Dental schools in Canada admit only 20–100 students per program annually, making strong academics and extracurriculars critical.
- Provincial Variations:Every province regulate their licence process and to permit the dentist to practice in their province , so contact the regional DRAs directly to get upto date information. .
Tips for success
- Plan Early: Map out prerequisites and timelines in high school or early undergraduate years.
- Network: Connect with practicing dentists for mentorship or shadowing opportunities or find online mentorship program.
- Stay Updated: Follow NDEB and DRA websites for changes to exams or licensure rules.
- Financial Planning: Financial planning is must , as licensure process is long , you have to preplanned you budget . You may get loan from banks or you must have savings in your account to complete whole licence path smoothly without any financial hurdle . For financial budget you can take help of dentists who have recently completed the licence process or you can contact to different schools who provide the dental education , as i have already listed in paragragraph 4
- Resilience: The journey is demanding, so maintain focus and seek support from peers or advisors.
Conclusion
Becoming a licensed dentist in Canada is an excellent but fulfilling path that combines academic excellence, clinical skill, and regulatory compliance. By following the outlined steps in becoming a dentist—from high school preparation to NDEB certification and provincial licensure—aspiring dentists can achieve their dream International dentists, through the NDEB Equivalency Process or bridging programs, have clear pathways to certification, along with they may face additional challanges . With dedication and strategic planning and accurate authentic information, you can join the ranks of Canada’s dental professionals, enjoying both personal fulfillment and competitive dentist salaries in Canada.
For further information, visit:
- National Dental Examining Board of Canada: ndeb-bned.ca
- Canadian Dental Association: cda-adc.ca
- Your provincial Dental Regulatory Authority